Co No3 2 6h2o Name
gruposolpac
Sep 13, 2025 · 5 min read
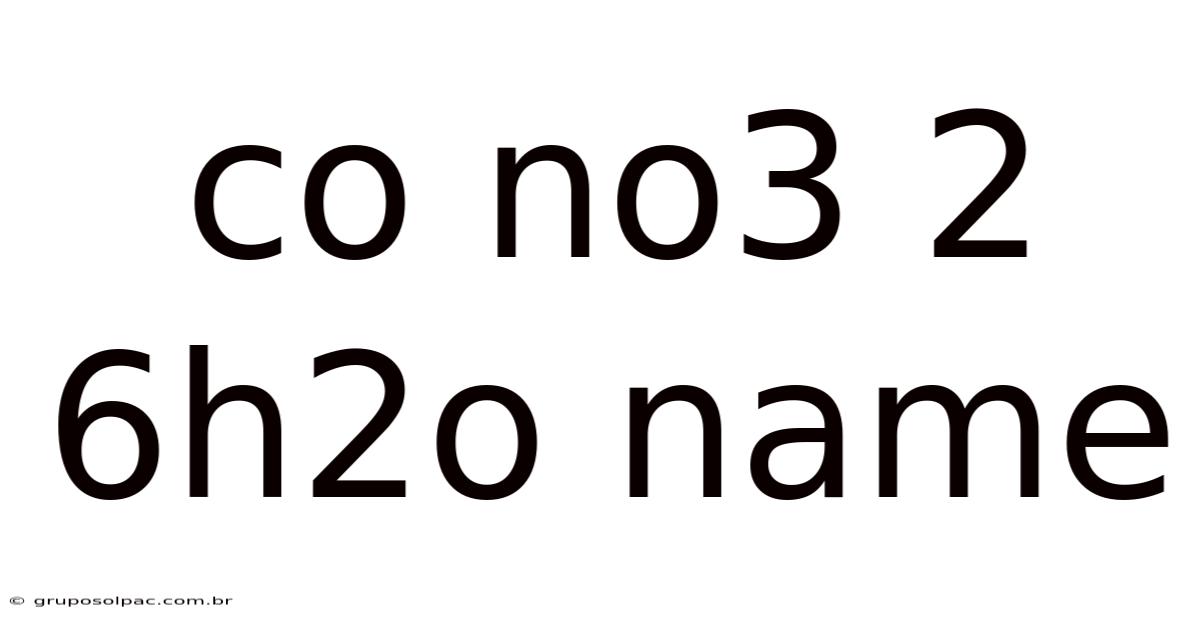
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mystery: A Deep Dive into Co(NO₃)₂·6H₂O
Introduction:
The chemical formula Co(NO₃)₂·6H₂O represents a fascinating compound, often encountered in chemistry labs and various industrial applications. This article delves deep into the identity of Co(NO₃)₂·6H₂O, exploring its common name, chemical properties, synthesis methods, uses, safety precautions, and related aspects. Understanding this compound requires a solid grasp of its chemical structure and behavior, which we'll explore in detail. This detailed analysis will provide a comprehensive understanding, exceeding the typical superficial overview often found. Let's unravel the secrets of cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate.
What is Co(NO₃)₂·6H₂O?
Co(NO₃)₂·6H₂O is chemically known as cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate. The name itself offers valuable information about its composition. Let's break it down:
- Cobalt(II): This indicates the presence of cobalt (Co) as a central metal ion, specifically in its +2 oxidation state. This means each cobalt atom has lost two electrons.
- Nitrate: NO₃⁻ represents the nitrate anion, a polyatomic ion with a -1 charge.
- Hexahydrate: The "hexa" prefix means six, and "hydrate" indicates the presence of water molecules bound within the crystal structure. Therefore, six water molecules are coordinated to each cobalt(II) nitrate unit.
This coordination of water molecules significantly influences the compound's physical and chemical properties. The hydrated form is the most common and stable form encountered.
Chemical Properties of Cobalt(II) Nitrate Hexahydrate
Cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate possesses several key chemical characteristics:
- Appearance: It's typically found as reddish-brown, deliquescent (absorbs moisture from the air) crystals.
- Solubility: It's highly soluble in water, alcohol, and acetone, making it readily usable in various solution-based reactions.
- Melting Point: It melts at a relatively low temperature, decomposing before reaching a true melting point. The exact decomposition temperature depends on the heating rate and pressure.
- Reactivity: It acts as a source of cobalt(II) ions in chemical reactions. The nitrate anion can act as a ligand in coordination chemistry, binding to metal ions. It's also a strong oxidizing agent, especially at elevated temperatures.
- Hygroscopic Nature: Its hygroscopic nature means it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere, potentially leading to changes in its composition and weight if not stored properly.
Synthesis of Co(NO₃)₂·6H₂O
Several methods can be employed to synthesize cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate. The most common method involves dissolving cobalt(II) carbonate or cobalt(II) oxide in dilute nitric acid. The reaction is exothermic, releasing heat.
Reaction with Cobalt(II) Carbonate:
CoCO₃(s) + 2HNO₃(aq) → Co(NO₃)₂(aq) + H₂O(l) + CO₂(g)
The resulting solution contains cobalt(II) nitrate. Slow evaporation of the solution allows for the crystallization of Co(NO₃)₂·6H₂O.
Reaction with Cobalt(II) Oxide:
CoO(s) + 2HNO₃(aq) → Co(NO₃)₂(aq) + H₂O(l)
Similar to the previous reaction, slow evaporation will yield the hexahydrate crystals.
Uses of Cobalt(II) Nitrate Hexahydrate
The versatility of cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate makes it valuable in a wide array of applications:
- Electroplating: It serves as a key component in cobalt electroplating baths, producing a protective and attractive cobalt coating on various metal substrates.
- Catalysis: Its catalytic properties find use in various organic reactions, particularly oxidation and reduction processes. It can act as a homogeneous or heterogeneous catalyst depending on the reaction conditions.
- Pigment Production: Cobalt compounds, derived from cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate, are employed in the production of vibrant pigments for paints, ceramics, and inks. The color of the pigments can vary based on the other components present.
- Synthesis of Other Cobalt Compounds: It acts as a precursor for the synthesis of other cobalt compounds, providing a convenient and readily available source of cobalt(II) ions.
- Analytical Chemistry: It finds applications in analytical chemistry as a reagent in various analytical tests and assays.
- Agricultural Applications: In some specific niche applications, it has been investigated for its potential use as a micronutrient supplement in fertilizers for plants, providing cobalt, an essential trace element for certain biological functions. However, its use in this area is limited and requires careful consideration of environmental impact.
Safety Precautions and Handling
Cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate, like many chemicals, requires careful handling to ensure safety:
- Eye and Skin Protection: Always wear appropriate safety goggles and gloves when handling this compound to prevent skin and eye irritation.
- Inhalation: Avoid inhaling dust or fumes, as they can cause respiratory irritation. Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Ingestion: Do not ingest the compound. In case of accidental ingestion, immediately seek medical attention.
- Storage: Store the compound in a tightly sealed container in a cool, dry place away from incompatible substances. Keep it away from direct sunlight and sources of ignition.
- Disposal: Dispose of the compound according to local regulations and guidelines for hazardous waste disposal.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate toxic?
A: Yes, cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate is considered toxic if ingested or inhaled in significant quantities. It can cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. Proper handling and safety precautions are essential.
Q: Can cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate be heated to remove the water molecules?
A: Yes, heating cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate can remove the water molecules, leading to the formation of anhydrous cobalt(II) nitrate, Co(NO₃)₂. However, this process should be conducted carefully, as it can lead to decomposition at higher temperatures.
Q: What is the difference between cobalt(II) nitrate and cobalt(III) nitrate?
A: The difference lies in the oxidation state of the cobalt ion. Cobalt(II) nitrate features cobalt in the +2 oxidation state, while cobalt(III) nitrate features cobalt in the +3 oxidation state. This difference influences their chemical properties and reactivity.
Q: What is the color of anhydrous cobalt(II) nitrate?
A: Anhydrous cobalt(II) nitrate is typically a blue crystalline solid, in contrast to the reddish-brown color of the hexahydrate.
Conclusion:
Cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate, Co(NO₃)₂·6H₂O, is a versatile and important compound with a wide range of applications. Its chemical properties, including its solubility and reactivity, contribute to its usefulness in various industrial processes and laboratory settings. Understanding its synthesis, uses, and safety precautions is vital for anyone working with this compound. Remember that proper handling and storage are paramount to ensuring safe and efficient usage of this significant chemical substance. This detailed exploration provides a comprehensive understanding exceeding typical summaries, offering a valuable resource for students, researchers, and professionals alike. Always consult relevant safety data sheets (SDS) for specific handling and safety instructions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Speech On Population In English
Sep 13, 2025
-
Mobile Ki Atmakatha In Hindi
Sep 13, 2025
-
Missing Those College Days Quotes
Sep 13, 2025
-
Intercalary Meristem Is Present In
Sep 13, 2025
-
Class 10 Science Ch 3
Sep 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Co No3 2 6h2o Name . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.